Gas and Electricity has become a part of our lives, Ordinary day to day life is almost unimaginable without continuous energy supply. But how much do you know about the UK energy market and your energy supply? This comprehensive guide will take you a tour into every corner of UK energy supply from its generation until it is utilized in your home.
UK energy supply in a nutshell
The UK energy supply system is composed of four main components. The energy generators, the national network, the local distribution centres and the energy providers. The energy market is fully privatized and companies involved in one or many of these components. These companies are regulated by the government body Ofgem.
The households receive energy in the form of gas and electricity and it is generated from non-renewable (coal, fossil gas, nuclear power) and renewable sources (solar power, wind, wave ) within and outside the UK. The generated energy is bought by the energy suppliers and added to the national network and from there to the local distribution centres. These local distribution centres deliver gas and electricity to our homes.
customers have the liberty of selecting their own energy provider and a suitable energy plan (Energy tariff). The energy providers buy energy from the generators to match their consumption and add to the national network. Customer pays the energy provider for the energy they use. The catch is that the amount you pay for a unit of energy depends on the provider and the tariff you choose. The difference can be up to £500 per year for an average customer.
Fortunately, you have the option of switching your energy provider anytime you want. The UK government encourage energy switch and people who switch energy regularly ( at least once a year) stays in best energy deals.
The energy regulator Ofgem monitors the Uk energy market to protect the customers and loads of help and supports available when you face difficulty in relation to energy
The national grid

The national grid is the core of the UK energy system. It controls the central network which distributes gas and electricity across the country
National grid owns high voltage transmission network in the UK which consists of 4481 miles of overhead electricity lines and 1391 miles of underground electricity cables. National grid system operator (ESO) balance the system second by second and make sure homes and businesses supplied with electricity 24/7
National grid gas transmission system owns 4740 miles of high-pressure gas transmission pipes and transport gas from origin to local distribution points to match the day to day needs
Electricity generation in the UK
The UK is fairly self-sufficient in energy. In the first-quarter 2020, 94% of the energy was generated within the country and 5.8 % was exported via interconnectors of the national grid.
Electricity generated in power stations connected to the national transmission network. These are owned by different companies ranging from large multinational companies to small family-owned businesses.
Historically fossil fuel genrators lead the uk energy market. But there was a significant shift towards the renewable energy generation in the recent past
According to Ofgem renewable sources contributed to about 50% energy generation in 2020
| Coal | 3.1 % |
| Gas | 26.76 % |
| Oil | 0.17 % |
| Nuclear | 11.90 % |
| Hydro | 2.28 % |
| Wind and solar | 41.04 % |
| Bioenergy | 8.81 % |
| Pump storage | 1.59 % |
| Net Imports | 5.80 % |
The Local Distribution Networks operator (DNO)
DNO owns the infrastructure which connects the central energy network to your home and other local properties. The distribution network operator is not involved in billing for your energy. They can help you with connecting your house, In an emergency power cut or if you won’t move your meter.
Electricity Distribution Network Operators
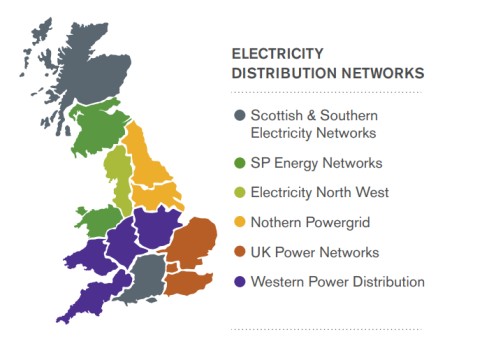
Fourteen network operators owned by six groups handle the local electricity distribution
| DNO Group | DNO |
| 1.SP Energy Networks | SP Manweb plc |
| SP Distribution plc | |
| 2.UK Power Networks | Eastern Power Networks plc |
| London Power Networks plc | |
| South Eastern Power Networks | |
| 3.Western Power Distribution | WPD (East Midlands) plc |
| WPD (South Wales) plc | |
| WPD (West Midlands) plc | |
| WPD (South West)plc | |
| 4.Electricity North West Limited | Electricity North West Limited |
| 5.Northern Powergrid | NP (Northeast) Limited |
| NP (Yorkshire) plc | |
| 6.Scottish & Southern Electricity Networks | Scottish Hydro Electric Power Distribution plc |
| Southern Electric Power Distribution plc |
Gas distribution network operators
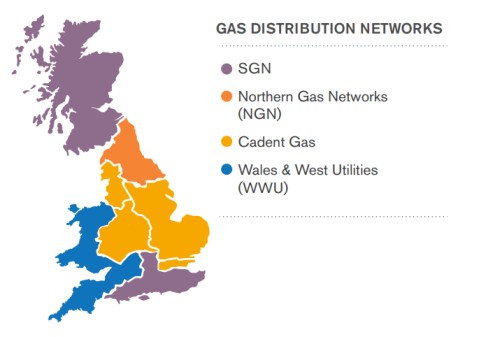
UK gas network operated by 8 networks owned by four groups
- SGN – Scotland, Southern
- Northern gas Network limited – Northern
- Cadent Gas Ltd – East of England, North London, North West, West Midland
- Wales and West Utility Limited
Energy companies
Energy suppliers deal directly with the customers. They buy energy from the wholesale market and sell it to the customers .currrenty there are about 60 energy companies compete to offer you their service. You can choose your gas and electricity supplier and the amount you pay for a unit of energy widely varies with the supplier you select. Whoever your supplier is you will have the same electricity cable network and gas pipelines and both gas and electricity comes from the national network. You supplier will purchase gas and electricity to match your consumption and add to the national network and charged it back from you.
Big six energy companies
The six companies EON. Scottish Power, SSE ( brought by OVO energy), EDF energy, n power, and British gas dominate the UK energy market and call the big six energy companies.
Collectively these 6 companies supply mare than 50 million homes in UK.
British gas – British Gas is the largest energy supplier in Uk and currently powers 15 million UK homes. It is the greenest energy supplier out of big six
EDF Energy – this is a french owened company and powers 5.6 milloon Uk homes
Eon – Up to date EON has 15 million customers and owned by a german energy firm
SSE – This is brought by the privately owned company OVO
Scotish power – owned by a Spanish energy firm ………..
npower – owned by a german energy firm
| Company | market share |
| British gas | 18.40 % |
| EDF Energy | 10.60 % |
| Eon | 12.10 % |
| n power | 6.70 % |
| Scottish power | 9.20 % |
| SSE (now owned by Ovo) | 15.80 % |
Small and medium size energy supplies
Contribution to the UK energy market from small and medium-size energy companies cannot be overlooked. These companies started invading the energy market after 1997 and currently holds a significant market share.
These companies have significantly cheaper tariffs compared to big six energy companies and they have further attracted the customer with more reachable customer services. In fact, during the last few years, these companies had higher customer ratings in customer review sites when compared to the big six companies.
A significant number of these small and medium-sized energy firms offer 100 green electricity and most of the offer carbon offsetting of their gas.
an increasing number of customers are now shifting from big six companies to the smaller firms. However, one main concern people have is the instability of some of these firms. Few energy companies went out of business during the last few years. In such extreme situations, customers are protected from Ofgem safe net and your energy supply is maintained without interruption.
read my energy supplier gone out of business – Ofgem
list of small energy suppliers.
| Energy supplier | Market share | 100% Green energy |
| Affect Energy | ||
| Avro Energy | 1.40 % | |
| Atlantic | ||
| Better Energy | ||
| Bristol EnergyCo-operative Energy | ||
| Bulb Energy | ||
| Cardiff Energy Supply | ||
| Co-operative Energy | ||
| E.On | ||
| Ecotricity | ||
| Economy Energy | ||
| Engie | ||
| Extra Energy | ||
| Fairerpower | ||
| Flow Energy | ||
| Future Energy | ||
| GB Energy | ||
| GEN4U | ||
| Glide | ||
| GnERGY | ||
| Go Effortless Energy | ||
| Good Energy | ||
| Green Energy | ||
| Green Star Energy | ||
| Green Network energy | 1.20 % | |
| Iresa Limited | ||
| iSupplyEnergy | ||
| LoCO2 Energy | ||
| M&S Energy | ||
| National Gas | ||
| Octopus Energy | 4.90 % | |
| Oink Energy | ||
| Pure Planet | ||
| Peterborough Energy | ||
| Places for People Energy | ||
| Robin Hood Energy | ||
| Sainsbury’s Energy | ||
| Shell Energy | 2.90 % | |
| SO Energy | ||
| Southend Energy | ||
| Spark Energy | ||
| SSE Airtricity | ||
| SSE Southern Electric | ||
| SSE SWALEC | ||
| The Energy Deal | ||
| Together Energy | ||
| TOTO | ||
| Tonik Energy | ||
| Utilita | 2.60 % | |
| Utility Warehouse | 1.90 % | |
| White Rose Energy | ||
| Zog Energy | ||
| Yu Energy |
GREEN ENERGY IN UK
With the rising concerns about the environmentally friendly lifestyle and constant pressure from environmental organizations, the world is moving toward green energy. Uk is embracing this positive current trend
energy is considered green when it is generated from renewable sources or when co2 produced from fossil fuel burn is balanced with environmental programs ( carbon offsetting)
green electricity
UK green electricity is produced from Wind power, solar power, hydropower. Renewable sources contribute to 40% of Uk energy making some energy firm offer 100% green energy. Whereas others offer 100% green electricity tariffs in addition to their nonrenewable energy tariffs
green gas
Green gas or biomethane is a perfect alternative to fossil fuel gas. It is produced from biodegradation of farm waste and food waste. .Unfortunately green gas is not as abundant as green electricity. green energy Uk is the only energy provider witch offers 100% green gas in Uk. most of the green energy suppliers try to offer at least 10% of their gas as green gas. However, the majority of these companies carbon offset their fossil fuel gas
carbon off setting
Carbon offsetting is the process of converting dirty gas into clean energy. In carbon offsetting, energy firms invest in a variety of approved environmental projects to reduce carbon dioxide to match the amount release from fossil fuel burn
How customers Select their supplier
The customers have absolute freedom to choose their own energy provider and change it whenever they need. As the energy market is highly competitive you have heaps of options to select from.
Price of gas and electricity varies from supplier to supplier and from tariff to tariff within the same supplier. So the customers should be vigilant if they want to controller what they pay for energy.
What is energy tariff and What options you have
Energy tariff is the energy scheme you are in with your provider. It explains how much you pay for your gas and electricity and how your supplier is going to bill you. Most energy companies offer several energy tariffs to meet different need and expectations of customers.
- Fixed-price energy tariff – in this type of tariffs price of a unit of gas or electricity is fixed for a pre-agreed period. Generally, fixed tariffs are the cheapest in the market.
- Variable-rate energy tariffs – In variable tariff energy price change with the market wholesale market price of the energy. these are usually expensive but there is no fixed contract period so the customer can switch anytime
- Dual fuel tariffs – means customer buys gas and electricity from the same supplier. some providers give dual fuel energy discount and you will have to deal with only one company.
- Green tariffs – in a green tariff all the energy perches on behalf of you will be from renewable sources so you are staying environmentally friendly
- Prepayment tariff – in prepayment tariffs customer to pay for energy beforehand similar to pay as you go mobile phones. Prepayment tariffs are comparatively expensive.
- Economy tariffs – Economy tariffs charge less for energy during off-peak hours in the night time so suitable for people using most of the energy during the night
Read more on energy tariffs explained
What is an energy switch and how to switch
Uk energy market is highly competitive and the price fluctuates pretty frequently. If you don’t want to pay unnecessarily you have to stay allert and shop for better deals periodically.
If you stay with the same supplier too long you will end up spending more. So you need to compare and switch the supplier at least once a year. Energy comparison and switching is a simple process and can be done completely online under 10 minutes. All you have to do is log in to one of the Ofgem accredited energy comparison websites and get a quotation. once you select your new provider the comparison site ( or new provider) will handle the switching process and you will be notified once everything is completed.
list of comparison sites
- Energy Helpline
- Money Supermarket
- My Utility Genius
- Energylinx
- The Energy Shop
- Quotezone
- Unravel It
- Runpath
- Simply Switch
- Switch Gas and Electric
- Uswitch
our recommended comparison site
Energy meters
The energy meter is the indicator of gas and electricity you use. Smart energy meters will send the meter readings directly to the energy supplier but for other meters, the customer has to take the meter reading and send it regularly to the energy provider.
Types
- Smart energy meters – these are new generation energy meters directly link to the supplies. Customer will get an in house display so they can have a precise understanding of daily usage and control their energy consumption. Uk is planning to install smart meters in every house by 2024.
- standard energy meters – this is the most common type reading is showed in a mechanical display
- Dial meter – looks similar to a clock and has six dials
- digital meter – shows the reading on a display.
- Economy seven and economy ten meters – These special meters will be installed if you have economy tariffs
- Prepayment meter – Prepayment meters allow you to pay for energy in advance in a way of key, card or token
how to get a reading
Ofgem the energy regulatory body
Ofgem is an independent national regulatory authority of the gas and electricity market. Its role is to protect customers and striving toward developing greener and fairer energy system. Ofgem is involved in policy decisions including price regulations and enforcements. Companies need Ofgem licence to operate in the UK energy system
What determines the energy price
Your energy bill depends on the number of units you use. But what determines the price of a unit? about 40% of the unit price is determined by the wholesale price of the energy your supplier buys. The balance is decided by the Network and balancing cost, cost of government obligations, supplier cost and profit and of course by the competition.
The price cap for energy
Marked variation of energy price from supplier to supplier means that one can end up paying a considerable extra amount for energy if they select an expensive supplier.
The price cap was introduced to make sure you pay a fair price for your gas and electricity and prevent you from overcharging. Twice a year February and Augusts Ofgem sets the price cap. The price cap is applied to a unit (kilowatt-hour) of energy and not for your bill. Energy suppliers cant charge more than that for energy but can charge less. That doesn’t mean your energy bill can’t go up or down. If you use more units of energy your bill can go high.
Ofgem updates the level of price cap every 6 months depending on the wholesale price of the energy. If the price goes up price cap is set high and if the price goes down price cap is set low. Price cap varies from area to area, the type of tariff you on ( prepayment or standard) and method of bill payment.
Price cap doesn’t guarantee that you pay lowest for the energy it only ensures that the maximum you pay is below a certain amount. You are likely to save more by switching the energy supplier regularly.
Support Schemes for energy
Support schemes are available to protect the vulnerable citizens
1.Warm Home Discount Scheme
Under the warm home discount scheme, you can get £140 off your electricity during winter. To get this discount your energy provider should be a part of the scheme and you should get guarantee credit element of pension credit or you should be on a low income. The amount is directly paid as a one-off discount on the electricity bill.
2.Cold Weather Payment
Cold weather payment exit as compensation to the extreme weather situation. If the temperature in the area is less than zero degrees for consecutive seven days you can get £25 payment. to be eligible you should be getting certain benefits or mortgage interest support
3.Winter Fuel Payment
With the winter fuel payment, you can get £100-£300 to support your heating bills if you are borne before 5th October 1954. If you are eligible you will get the payment automatically. If this doesn’t happen you have to make a claim.
Can not afford for energy
When a customer has difficulty in paying their energy bills they should first contact their suppliers. Energy companies should take their customer’s situation in a fair manner and should try to work out a plan for them
but if they need further assistance they can contact
- National Debtline
- Money Advice Service
- Money & Pensions Service Money Navigator Tool
- StepChange Debt Charity
following charitable funds can help with energy debts
- British Gas Energy Trust
- EDF Energy Customer Support Fund
- Scottish Power Hardship Fund
- Bulb Energy Fund
- npower Energy Fund
- Ovo Debt and energy assistance
- E.on Energy Fund
Compensations for customers
Strict rules and regulations exist to safeguard customer rights. You are eligible for compensation in the following situations
- Erroneous energy switch
- energy supplier fails to send your last bill within 6 weeks after an energy switch
- Your old supplier fails to refund any money owed to you within 10 working days after the last bill
- Energy switch not completed within 15 working days
- Unplanned power cut
- planned power cut without sufficient prior notice
Read more
- Switch craft review
- Weflip review
- Cheap energy club review
- How to switch energy supplier without penalty
- 10 Energy myths busted
- Best energy comparison website – a market research
- Cheap green energy
- How to switch energy supplier and find the best deal
- Energy tariff explained
- How to set up gas and electricity in a new home
- Utilitypoint review
- Bulb energy review
- Octopus energy review
- so energy review
- Billbuddy reviews
